 Overview
Overview
Version: 1.2 | Release Date: 07/02/2024
Precaution
- Not overwriting any aiM18's SQL procedure.
- Not modifying/removing existing aiM18 table's fields.
- All SQL field name/procedure name should prefix with app code .
_should not be used as table/field name.
# Things to know
The aiM18 platform is only licensed to Multiable's customers and third-party certified developers. Developing an app requires an authorized aiM18 platform.
If you have questions, please contact Multiable's implementation consultant or ask your question in our forum (opens new window).
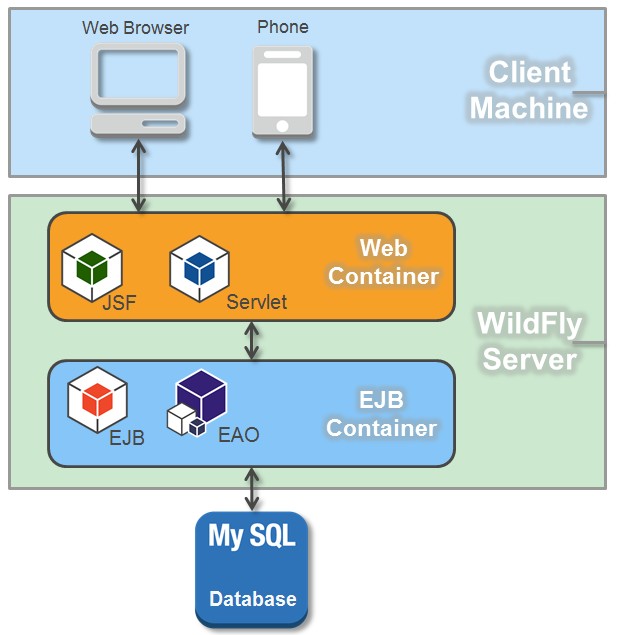
# aiM18 Architecture
aiM18 platform is developed based on J2EE and is deployed using WildFly (Java EE Server). aiM18 uses JSF, a component based web framework, for front-end development and EJB, a server-side software component, for back-end development. It uses MySQL as database.
WildFly, which is written in Java and implements the Java EE, is an application server authored by Red Hat (Original by JBoss). Familiarity with the configuration and function of WildFly will enhance developing, tuning and debugging.
EJB is a server-side software component that encapsulates business logic of an application. You can imagine EJB as a group of modules which contains different parts of business logic. It serves as a standard to handle issues that happen repeatedly. In aiM18, EJB receive requests from JSF and search for data in MySQL database if necessary.
# aiM18 App Concept
aiM18 is a combination of a low-code rapid development platform and some built-in App features.
Third-party developers can extend these existing features or add new features by developing their own apps.
App is a group of specific functions which can be managed and maintained separately. Different Apps can be grouped together to form a Web Application.
# App development tutorial
To develop the aiM18 App, you need a complete set of run-time aiM18 programs, including WildFly and databases and aiM18 packages.
If multiple developers are developing on an aiM18 instance at the same time, the database is usually shared, and WildFly is a copy for each developer.
Your development environment should be a separate set of software independent of the production environment. Usually a user test environment installed with the production environment.
You'd better set up a development environment before continuing to read other content, which will give you a better understanding of other content.
# About app.xml
Each App has an xml file called app.xml that describes various attribute information of the App.
For the path of the app.xml, please refer to our example on Github (opens new window)
| Name | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | Y | Unique key; name of the App |
| version | Y | Format: d.d.d_*** d is a number; The version number can only be increased |
| description | N | Description of the App |
| mess | Y | MessCode used in UI |
| ear | Y | Name of the ear; Must be caw_ear currently |
| ejb | Y | Name of the EJB jar |
| appLogoName | Y | Logo name in UI |
| appLogoLib | Y | Logo location in UI |
| developer | Y | Name of the developer in UI |
| developerLogoName | Y | Logo of the developer in UI |
| developerLogoLib | Y | Location of the logo of the developer in UI |
| dependences | N | Describe the dependences of the App |
| *** | Other attributes will be explained in other sessions |
Example:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<app xmlns="http://www.multiable.com/app">
<name>m18 test</name>
<version>1.0</version>
<description>test</description>
<ear>caw_ear</ear>
<ejb>core_ejb</ejb>
<dependences>
<dependence id="caw" version="1.0">
</dependences>
</app>
# Glossary
Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Module | aiM18 Module is similar to domain model in Domain-driven design. |
| Menu | A View entry of the Module, each Module can have multiple views with different layout and permission controls. End users can also define their own Menu and related View layout. |
| SqlEntity | Sometimes abbreviated as Entity, one record of the Module, represented by an instance of SqlEntity. |
| SqlTable | An instance of SqlTable that corresponds to a row of records in a database table. |
| Lookup | Means search in aiM18, includes the conditions of the query, the columns displayed, the scope of the keyword query |
| Mess | The abbreviation of Message, please refer to i18N Implementation |
# Module
The Module is a representation of meaningful real-world concepts pertinent to the domain that need to be modeled in software.
The concepts include the data involved in the business and rules the business uses in relation to that data.
For example, Customers, Sales Orders, Employees, Warehouses, Departments
aiM18 use xml file named module.xml to describe Module, please refer to module.xml for detail.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<module name="virDept" mess="virDept" extend="false" mainTable="virdept" useChangenote="true" genCode_Type="VO" recType="" useAccess="true" useAttach="true" useApv="true">
<table name="virdept" key="code" initRow="1" hpk="" fKey="" hfName="" hfKey="" order=""/>
<table name="virdeptpic" key="id" initRow="0" hpk="hId" fKey="picTypeId;userId;startDate" hfName="" hfKey="" order="" cpnType="table"/>
<table name="virdeptmember" key="id" initRow="0" hpk="hId" fKey="" hfName="" hfKey="" order="" cpnType="table"/>
<checker class="com.multiable.core.ejb.checker.VirDeptChecker"/>
</module>
# Menu
aiM18 use xml file named navmenu.xml to describe Menu, please refer to navmenu.xml for detail.
<folder code="language" messCode="core.lang">
<menu code="langSetting" messCode="langSetting" src="view/module/langSetting" mType="SETTING">
<function name="Save" />
</menu>
<menu code="udfMess" messCode="udfMess" src="view/module/udfMess">
<function name="Save" />
<function name="DataImport;DataExport" />
</menu>
<menu code="i18nFieldSetting" messCode="i18nFieldSetting" src="view/module/i18nFieldSetting" module="i18nFieldSetting" mType="SETTING">
<function name="Save" />
</menu>
</folder>
# SqlTable
Based on the extensible feature of aiM18, SqlTable is created to be a common data carrier for data storage.
SqlTable consists of table name (not necessarily equal to the table name in database), column information as wall as data.
aiM18 use xml file named datadict.xml to describe SqlTable, please refer to datadict.xml for detail.
<table name="useremailsender" mess="emailSender" pk="id">
<inherit name="id_irev" />
<column name="hId" type="int_unsigned" mess="user" defValue="0" defPattern="user" />
<column name="mailUser" type="varchar" mess="core.mailUser" length="100" defPattern="char100" />
<column name="mailPwd" type="varchar" mess="core.mailPwd" length="2000" defPattern="char2000" skipLookup="true" dataExport="false"/>
<column name="mailAccount" type="varchar" mess="core.mailAccount" length="100" defPattern="char100" />
</table>
Note:
1. Please ensure the data in SqlTable can be transfered to JSON as the system will use JSON format in operation.
2. aiM18 does not recommend storing a SqlTable or other non-primitive type data into SqlTable.
# SqlEntity
SqlEntity is a common data carrier to save, read, update or delete the modules defined in module.xml.
SqlEntity consists of the current module name and a group of SqlTables.
Note:
1. A `mainTable` must exist in SqlEntity and aiM18 will consider the `id` in the `mainTable` to be `id` of the SqlEntity.
SqlTable's common operation
Retrieve Data from Database
SqlTable data = CawDs.getSqlResult("select * from test where code like 'B%';");
Create New Table
SqlTable data = new SqlTable();
data.setName("test");
data.addField(new SqlTableField("info", String.class));
data.addField(new SqlTableField("check", Boolean.class));
// or
SqlTable data_new = data.genEmptyTable();
Add Row and Assign Value
int row = data.addRow();
data.setString(row,"info","test");
Table Loop
for(int row : data){
String info = data.getString(row,"info");
}
Append Tables
SqlTableLib.append(src, inc);
Create Table Indices
Integer[] indexs = SqlTableLib.getIndex(sortFields, data);
Note:
1. Please refer to the classes `SqlTable` and `SqlTableLib` for most of the SqlTable's operation.
# Lookup
Each Module's Menu will have a Lookup by default, and the end user can also define their own Lookup.

When you reference the data of another module in one module, the query used is also defined by Lookup.
The implementation of Lookup is defined by stInfo.xml and stSearch.xml.
CheckMsg
Almost all error messages in aiM18 use the class CheckMsg.
CheckMsg mainly consists of:
info_desc: Message displayed in user interface. Should not contain any mess code.
trace: Information about where this CheckMsg is created.
MsgLocator is used to define which field(s) causes the error.
Note: Please refer to CheckMsgLib for displaying messages in aiM18.
