 Create Module Data
Create Module Data
Version: 1.2 | Release Date: 07/02/2024
# Introduction
Essentially, there are two methods for creating a Module Record.
The first method involves constructing it from the ground up based on the Module Data Dictionary’s specifications and filling in all necessary information.
The second method involves obtaining an entirely empty structure through the API and then consulting the data dictionary to fill in the necessary fields.
We recommend the latter approach.
# Aim
After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
- Create a module record through Web Service
- Understand Data Dictionary in aiM18
- Mastering best practice to create a module record
# Scenario
Chris Wong is IT Manager of ABC Fruit Company. Customers can order fruits from the Online Shop:
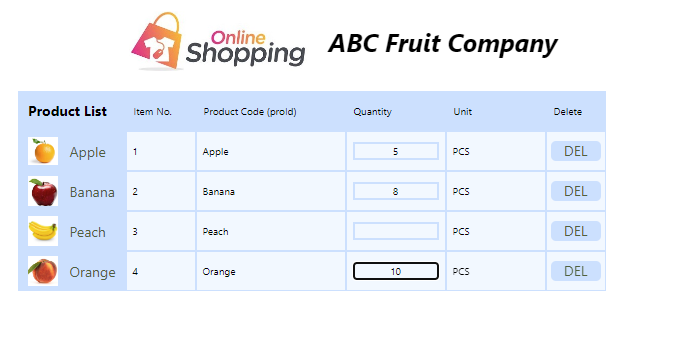
Chris collects orders received from online shop every day and passes data to Sales Department for data entry into aiM18 ERP System.
Manager of Sales Department complaints that data volume is too huge.
It is very time consuming to input data manually.
Other than using importation provided in aiM18 ERP System, Chris decides to automate this process with the help of Save Entity Service.
# Refer to the document
The following content demonstrating how to save a record to a specific module.
Please refer to the complete documentation here.
HTTP Request
PUT http://[server]/jsf/rfws/entity/s/save/[module]?menuCode=[menuCode]
Parameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| authorization | String(Header) | Required. Access Token obtained via OAuth |
| client_id | String(Header) | Required. Client ID in aiM18 OAuth Applications |
| module | String(Path) | **Required. **Module type,such as 'employee', can be found in data dictionary. |
| menuCode | String(Query) | Required. Menu code, such as 'employee', can be found in data dictionary. |
| param | jsonString(Query) | Additional parameters for special actions. |
| entity | jsonString(Query) | The Simplified Entity JSON, structure please refer to the below. Notice that the JSON need to be URL Encoded. |
| entitys_in_entity | String(Body) | The Simplified Entity JSON, structure please refer to the below. It is recommended to pass entity JSON in request body.If you want to handle more entitys, please pass an array of Simplified Entity JSON. |
Most of the parameters are intuitive and can be interpreted literally.
If you cannot find your authorization and client_id, please check here.
The parameter that we will concentrate on explaining in the following section is the entity.
entity is basically a JSON containing tables and values you are going to save.
Normally we get this by JSONising the SqlEntity.
{
"employeepic": {
"values": [ ]
},
"employee_attach": {
"values": [ ]
},
"employee": {
"values": [
{"code": "000171","desc": "abcd"}
]
}
}
By utilizing the Data Dictionary provided in aiM18, you can obtain all the necessary table information for the Module.
In this case, We need to fill in table Sales Order and S.O. (Product).
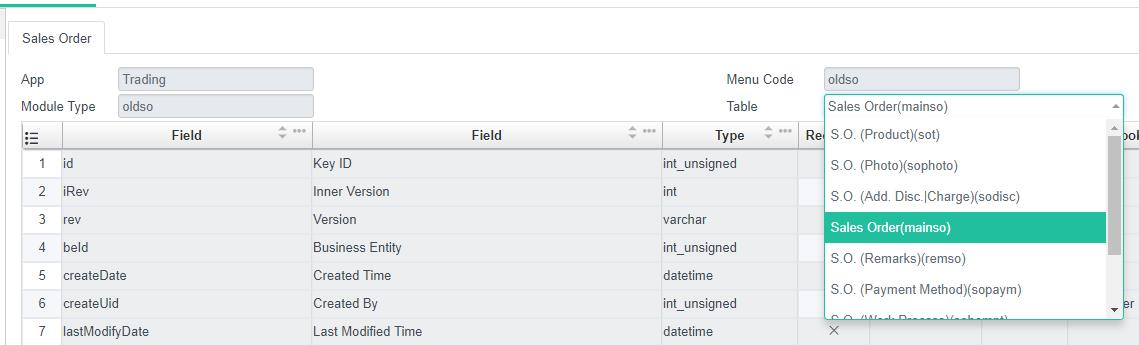
The table name of Sales Order is mainso.
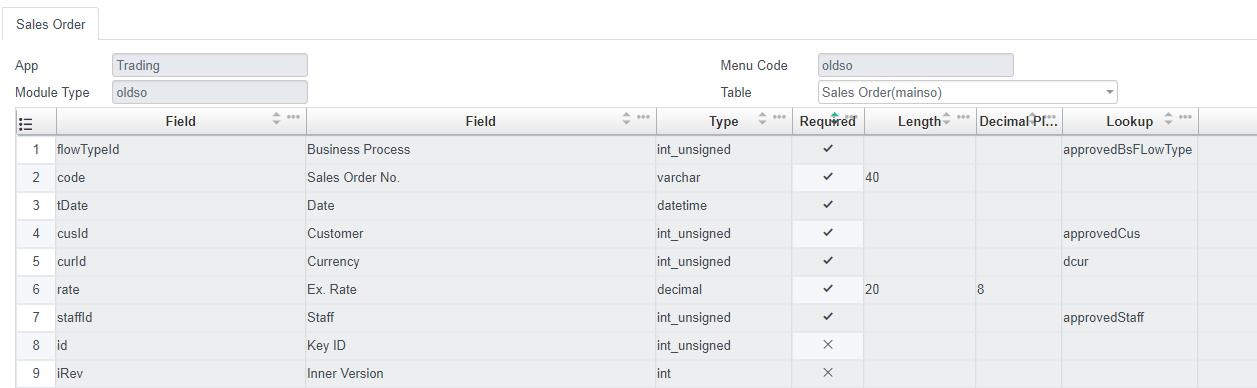
In order to save a SqlEntity successfully, we must at least input all the required fields marked.
All other fields are optional.
Sample Data as below
{
"mainso": {
"values": [
{
"flowTypeId": 1,
"code": "MYDEMOSO_001",
"tDate": "2018-08-10 00:00:00",
"cusId": 1,
"curId": 2,
"rate": 7.5,
"staffId": 11
}
]
}
}
FAQ 1:
How to find out cusId (Customer)? Move to FAQ Section for the solution.
The table name of S.O. (Product) is sot.
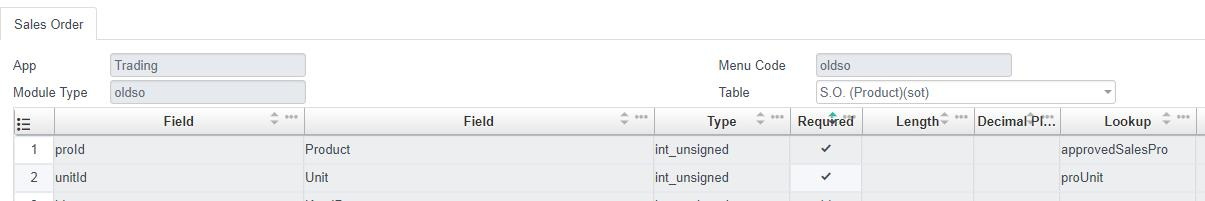
Again, fill in the required fields first and then the optional fields.
Sample Data as below
{
"mainso": {
"values": [
"flowTypeId": 1,
"code": "MYDEMOSO_001",
"tDate": "2018-08-10 00:00:00",
"cusId": 1,
"curId": 2,
"rate": 7.5,
"staffId": 11
]
},
"sot": {
"values": [
{
"proId": 1,
"unitId": 2,
"qty": 10
},
{
"proId": 2,
"unitId": 3,
"qty": 7
}
]
}
}
FAQ 2:
How to find out proId (Product) or unitId (Product Unit) ? Move to FAQ Section for the solution.
Now you should be ready to submit your request.
Back to the scenario, Chris integrates the Online Shop with aiM18 Web Service.
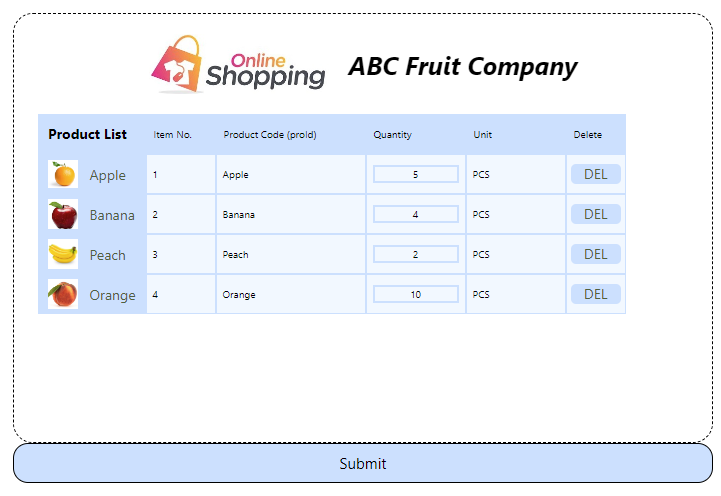
When an order is confirmed, below HTTP request is send to aiM18 ERP System.
Sales Order is saved automatically.
Corresponding Request:
MediaType jsonMT = MediaType.parse("application/json; charset=utf-8");
RequestBody rb = RequestBody.create(jsonMT,
{
"sot": {
"values": [
{ "proId": "1", "qty": "5", "unitId": "1" },
{ "proId": "2", "qty": "4", "unitId": "1" },
{ "proId": "3", "qty": "2", "unitId": "1" },
{ "proId": "4", "qty": "10", "unitId": "1" }
]
},
"mainso": {
"values": [
{
"flowTypeId": "1",
"code": "OLDSOOO1",
"tDate": "2018-01-01 00:00:00",
"cusId": "1", "curId": "1",
"rate": "1", "staffId": "1"
}
]
}
}
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://[server]]/jsf/rfws/entity/s/save/oldso?menuCode=oldso")
.put(formBody)
.addHeader("authorization", "Bearer MjZhZGNjMDctODVhZS00MmE0LWI3ZmEtNzRhMTQ")
.addHeader("client_id", "C-SGF2aWQncyBhcHBsaWNhdGlvbjIwMTctMDItMTAxNjc=")
.addHeader("cache-control", "no-cache")
.build();
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
Corresponding Response:
HttpResponseProxy{
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
[
Connection: keep-alive,
X-Powered-By: Undertow/1,
Server: WildFly/9,
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8,
Content-Length: 2,
Date: Thu, 09 Aug 2018 04:59:18 GMT
]
ResponseEntityProxy {
[
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8,
Content-Length: 2,
Chunked: false
]}
}
# Best practice
While you can get all the table and field information for a module through the Data Dictionary, this approach is still a bit cumbersome.
The best practice for creating a module record is to get an empty structure via another API and populate it with data.
The steps are as follows:
- Get an empty structure via API
- If you are programming in Java, you can convert the JSON result which return by previous API directly to a SqlEntity
- Manipulating the SqlEntity, such as modifying values and filling in rows of a table
- Convert the SqlEntity to JSON format, that's the
entityparameter of the Save Entity service.
# FAQ
- How to find out those xxxxId?
Web Service for finding ID is provided.
For detailed tutorial, Please refer to Get Id by Code Web Service or Search Data.
- How to understand the error info from the response?
You can read the error_info.messageData.info_desc for the exact reason.
If it is not clear enough, please enquire our Support and provide us the below error message from your response.
{
error_info: {
"autoClose":true
"closable":true
"delayClose":3000,
"detailSet":false,
"htmlMessage":false,
"locator": [ {"locator":"sot.qty."2"} ],
"messageData": {
"exception":"", "htmlMessage":false
"id":101203,
"info_desc":"<Quantity> of <Product> cannot be 0",
"jsonStr":"",
"key":"ce01_core_101203",
"locators": [ {
"colName":"qty",
"id":0,
"locatorKey":"sot.qty.2",
"row":2,
"tableName":"sot",
"type":"Field" } ],
"pass":false,
"trace":"
[TradeModuleChecker.checkSetting_791]-
[CheckerLib.runChecker_225]-
[CawEntityCurdAction.updateEntity_107]-
[CawEntityInterceptor.logCall_42]-
[view129.updateEntity_-1]
",
"type":"Error"
},
"messageKey":"ce01_core_101203",
"type":"ERROR"
}
}
