 Modify Module Data
Modify Module Data
Version: 1.2 | Release Date: 07/02/2024
# Introduction
In any modern transaction system, modifying data is always unavoidable.
It is essential to enhance user experience by providing a flexible editing environment.
# Aim
After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
- Read module records
- Update module records
# Scenario
Chris has done well with his ABC Fruit Company Online Shop.
He wants to improve user experience when customers need to change their order.
Customers have to call Chris and request for an order cancellation so that they can correct order content.
Chris would like to implement editing feature in the online shop.
Chris designs the layout as below, Users can switch by clicking on different order code to view the detailed information of Sales Order.
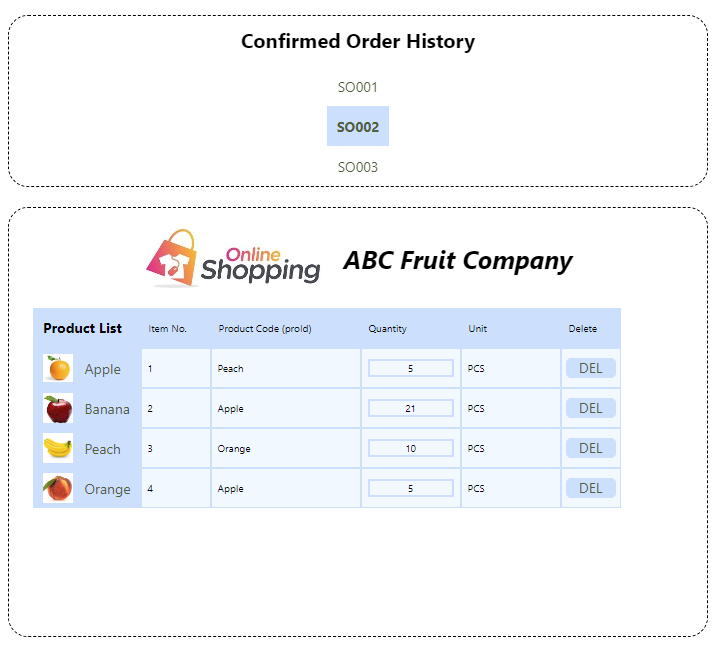
With past experience, Chris is able to list the saved order list using Search Services.
But how to display the product information of the order?
In order to achieve this goal, we need to call the Read Entity Services.
# Read module record
HTTP Request
GET http://[server]/jsf/rfws/entity/read/[module]?menuCode=[menuCode]&id=[id]
Parameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| authorization | String(Header) | Required. Access Token obtained via OAuth |
| client_id | String(Header) | Required. Client ID in aiM18 OAuth Applications |
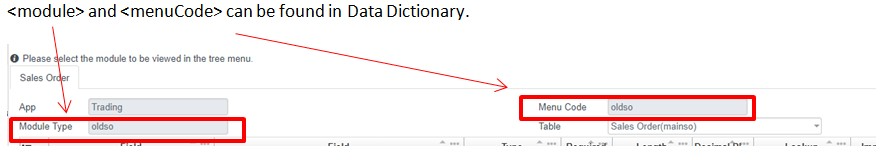
| module | String(Path) | **Required. **Module type, such as 'employee', can be found in data dictionary |
| menuCode | String(Query) | Required. Menu code, such as 'employee', can be found in data dictionary |
| id | long(Query) | Required. ID of the entity. |
| param | json String(Query) | Additional parameters for special actions |
| iRev | int(Query) | If you want to read the old version of the entity, please set this value. If you want to read a delete entity, please set the id and iRev of the delete entity. |
This service has three required parameters, which are module, menuCode, and id.
For id parameter, Please refer to Get Id by Code Web Service or Search Data.
In this scenario, the id should be included in the response of the search which used to display the sales order list.
Sample request to get info of Sales Order where Id = 2
GET
http://[server]/jsf/rfws/entity/read/oldso?menuCode=oldso&id=2
Sample Response
"mainso":"{
"size":1,
"values":[
{
"id":2, "iRev":1, "code":"SO002", ...
}
]
},
"sot":"{
"size":4,
"values":[
{
"id":3, "hId":2, "itemNo":" 1, "proId": 3, "bDesc":"Peach", "qty":5.0, ...
"id":4, "hId":2, "itemNo":" 2, "proId": 1, "bDesc":"Apple", "qty":21.0, ...
"id":5, "hId":2, "itemNo":" 3, "proId": 4, "bDesc":"Orange", "qty":10.0, ...
"id":6, "hId":2, "itemNo":" 4, "proId": 1, "bDesc":"Apple", "qty":5.0, ...
}
]
}
Reading existing orders is the not the end. We need to update orders when customers changed content.
We do this by calling the Save Entity Service.
# Update module record
Save Entity Services is capable of performing two functions, firstly creating a module record and secondly updating an already existing module record.
Regarding the creation of module record, we have already had a complete example earlier, please refer to Create Module Data.
So how does the system determine if the call is to add or modify a module record?
The answer is id.
The system will check if the request contains id information and the id information corresponds to the record in the database.
# Best Practice
Every time you want to modify an already existing module record, you read it first, then modify it directly in SqlEntity, and then call the Save Entity service to save it.
# FAQ
1.Is there an alternative method to determine whether this save action is creating a new record or modifying an existing one?
For APIs related to ERP, the answer is affirmative.
The code is another crucial field in aiM18 records. Users who designate this field as unique ensure that the code will not be duplicated.
Storing a record with an identical code is considered as an update.
